Callbacks, Sync vs Async and Event Loop
Exploring the concepts of callbacks, synchronous and asynchronous programming, and the event loop.

Jhonatas Matos
Understanding the event loop, callbacks, and async/await is essential for writing efficient JavaScript code. This post explores these core concepts with practical examples.
Why Understand the Event Loop?
✔ Write more performant applications
✔ Avoid common async pitfalls
✔ Debug timing issues effectively
✔ Choose the right async pattern for each scenario
Callbacks
Callbacks are functions passed as arguments to be executed when an async operation completes.
Basic Callback Pattern
function fetchData(callback) {
setTimeout(() => {
callback('Data received');
}, 1000);
}
fetchData((data) => {
console.log(data); // "Data received" after 1s
});
Common Pitfalls
// ❌ Callback Hell
loadUser(id, (user) => {
loadOrders(user.id, (orders) => {
loadDetails(orders[0], (details) => {
console.log(details);
});
});
});
// ✅ Using Promises
async function loadAll() {
const user = await loadUser(id);
const orders = await loadOrders(user.id);
const details = await loadDetails(orders[0]);
console.log(details);
}
Callback Called Multiple Times
// ❌ Risk of duplicate execution
function process(callback) {
callback('First call');
callback('Second call');
}
// ✅ Solution: Ensure single execution
function processSafely(callback) {
let called = false;
return (...args) => {
if (!called) {
called = true;
callback(...args);
}
};
}
Sync vs Async

Synchronous Code
Synchronous code runs sequentially, blocking the thread until each operation completes.
console.log('Start');
function heavyTask() {
console.log('CPU-intensive work');
// Blocks execution
for(let i = 0; i < 1e9; i++) {}
}
heavyTask();
console.log('End'); // Only runs after heavyTask()
Asynchronous Code
Asynchronous code allows other operations to run while waiting for a task to complete.
console.log('Start');
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Timeout completed');
}, 2000);
console.log('End'); // Executes immediately
// "Start", "End", "Timeout completed" after 2s
Key Differences:
Below is a comparison of synchronous vs. asynchronous execution, highlighting flow, thread blocking, and callback usage:
| Characteristic | Synchronous | Asynchronous |
|---|---|---|
| Execution Flow | Linear | Non‑linear |
| Blocks Thread | Yes | No |
| Callback Usage | Rare | Essential |
| Examples | Loops, calculations | setTimeout, fetch |
The Event Loop
The mechanism that manages code execution, callbacks, and events.
Core Components:
- Call Stack: Execution stack (LIFO)
- Web APIs: setTimeout, DOM events
- Callback Queue: Holds callbacks to be executed
- Event Loop: Orchestrates the process
Visual Representation:
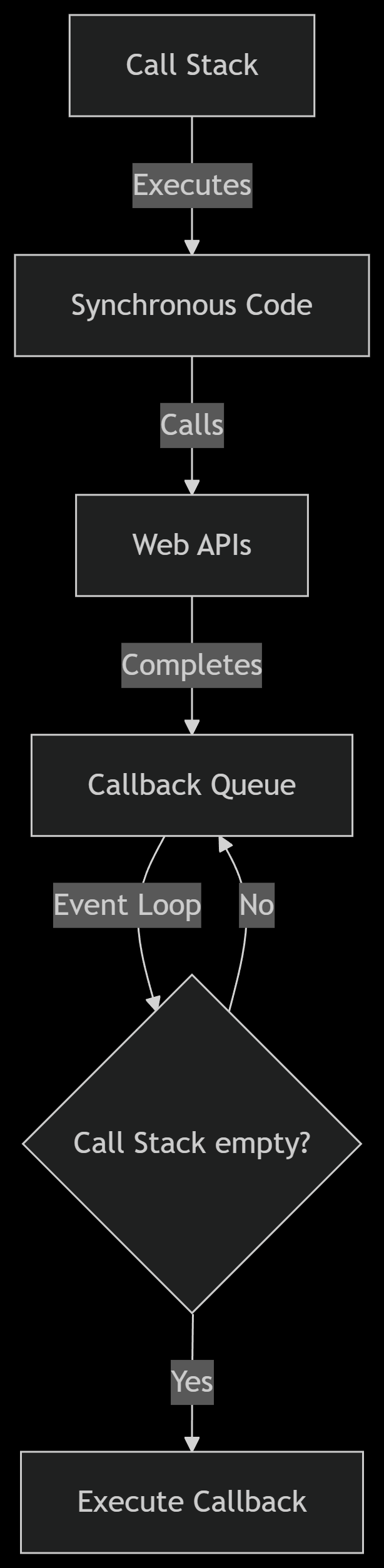
Practical Demonstration:
console.log('Script start');
setTimeout(() => console.log('setTimeout'), 0);
Promise.resolve()
.then(() => console.log('Promise 1'))
.then(() => console.log('Promise 2'));
console.log('Script end');
// Output:
// "Script start"
// "Script end"
// "Promise 1"
// "Promise 2"
// "setTimeout"
Execution Priority
This table shows how JavaScript schedules tasks: first synchronous code, then microtasks (Promises), and finally macrotasks (timers and events):
| Type | Examples | Priority |
|---|---|---|
| Synchronous | console.log, loops | 1 (highest) |
| Microtasks | Promises, queueMicrotask | 2 |
| Macrotasks | setTimeout, events | 3 |
Practical Use Cases
When to Use Callbacks:
- Simple DOM events
- Node.js I/O operations (legacy code)
- Libraries requiring callbacks
When to Avoid:
- Operations needing chaining
- Complex multi-step flows
- When Promises/async-await are available
Practice Exercise
console.log('1');
setTimeout(() => console.log('2'), 100);
Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log('3'));
console.log('4');
// What's the execution order?
Practical Exercise
Link to GitHub projectConclusion
Mastering callbacks, sync vs async, and the event loop is crucial for writing efficient JavaScript code. Understanding these concepts helps you:
- Write more performant applications
- Avoid common async pitfalls
- Debug timing issues effectively
- Choose the right async pattern for each scenario
Further Reading and Resources
- MDN Web Docs - Asynchronous JavaScript
- JavaScript.info - Promises, async/await
- You Don't Know JS (book series)
Videos
JavaScript Visualized - Event Loop, Web APIs, (Micro)task Queue (en)
JavaScript Event Loop: How it Works and Why it Matters in 5 Minutes (en)
Async, Promises, Callbacks, Event Loop - JS (pt-br)
Callbacks, Sincrono, Assíncrono e Event Loop no JavaScript (pt-br)